Businesses need to accept a great number of credit card payments made with a single tap. The process seems quite simple, with money moved from one bank to another in a few seconds. But what’s happening behind the scenes? What’s card acquiring and how it works? How does it get corporate payments processed smoothly and efficiently? Read on to learn the answers to these questions.

A credit card acquirer allows the merchant to receive online payments from their customers. It serves as the significant link between the e-commerce company and the card network, checking data and verifying the financial operation.
The payment processing may seem hard to figure out at first. The scheme below shows the flow of the customer’s finances to the acquiring bank account. To give you a better idea of how these two work together, here’s a step-by-step guide:
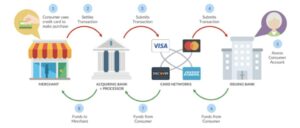

You need an acquirer and an issuer to pay for a purchase online. In fact, there are more parties involved in the payment ecosystem. Let’s explore the importance of each player in the card payment ecosystem.
What is the distinction between the issuing bank vs acquiring bank functionality? Both institutions play a significant role for online and offline businesses and the average consumers. The issuing bank is the financial institution on the consumer’s side. The card acquiring bank represents the merchant’s side. The collaboration between these two parties guarantees quick and safe transfers.
The issuer takes on liability on the customer’s side, while the acquirer stands on the merchant’s side of the transaction. The acquirer is going to exchange funds with different street banks each time a consumer buys products and services online, claims a refund, or receives a chargeback. The issuing bank goes between the credit card network and the card owner. It increases the customer’s line of credit, so the customer can make purchases and pay money back with interest.
The term “merchant acquirer” is often used instead of the term “payment processor”. These terms aren’t the same. The merchant acquirer is responsible for financial operations, ensuring funds are safely processed from the private account to the corporate one. The payment processor transfers data from the corporate account to the card acquiring bank and card provider. It submits the aggregated payment data to the card network and bank. In some cases, the processor may also establish payment terminals, allowing e-commerce companies to take payments in person.

Card acquirers and card providers like Visa and MasterCard deal with credit card transactions. They have different functionality and perform separate tasks. The acquirer collects payment data and contacts the relevant card issuer. After getting approved verification, the issuer will transfer money to the corporate bank account.
Card schemes help customers make purchases and pay bills without the need for real cash. They create universal standards for payment processing, establish strong safety protocols, and determine currency exchange fees. They connect the card issuers with the card acquirers. The card scheme relies on monitoring mechanisms to maintain the acquirer’s performance. It also monitors possible returns, refunds, and chargebacks.
The credit card acquirer aims to process payments under the best terms. By selecting the right acquirer, the merchant enables smooth transactions and secures a long-term partnership that will contribute to their commercial growth.
Not all acquirers can be trusted partners. Discovering the best one can greatly influence a business’s performance. Get familiar with the key factors to consider when choosing a card acquiring bank for your corporate needs.
You should look for the best way to optimize the data load on the card payment network. Some card acquirers complete quick transactions, while others take time to process. Pay attention to the transaction speed if you want to collect your money as soon as possible.
Acquirers charge merchants for completing credit card transactions. The service fee is usually set between 1% and 3% of the transaction value. There can be special fees charged by card networks and issuing banks. The fees for authentication or payment solutions shouldn’t be excluded as well. Knowing how much you are going to pay and to whom is significant. Compare the cost structure of different acquirers to choose the most reasonable solution for your type of transaction.
You should look for a credit card processor that would be compatible with the existing business system (e.g., e-commerce platform, point-of-sale (POS), accounting software, and other software. Check the compatibility of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), software development kits (SDKs), or plugins, reducing possible disruptions and optimizing transaction management.
If something goes wrong during or after the integration, you should be able to contact excellent customer service. Look for an acquirer with responsive and accessible support. Make sure you can get assistance with a basic transaction query or a complex technical issue.
Card acquiring is a complex process where several parties small tasks between several parties take place simultaneously. It requires technical knowledge to manage a merchant’s transactions efficiently. Merchants should collaborate with card acquirers with an overly positive rating. Check what other merchants say about this or that acquirer.
Make sure your credit card processor has strong compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), meant to secure card data. Any POS terminals or online payment portals should employ regulated data encryption technology to protect both you and your customers.
An acquirer should provide a detailed statement, detailing all financial operations made during the particular time period. The document will also include all the charges deducted by the acquirer and other costs, such as terminal hire and chargebacks. This kind of analytics can help you identify peak sales periods, improve inventory, and enhance marketing strategies.
Acquirers have different approaches to reporting financial metrics. Find out exactly what data you’ll get from your acquirer by the end of the month. Make sure it’s exactly what you need for your business.
Now that you know the key factors, you may check additional features as well. Consider those when choosing the right acquirer.

Credit card acquiring requires a unique position to serve the needs of various businesses. The most common industries include:

About 1.25 billion people, or 16% of the world’s population, use credit cards, to make online payments. The global credit card payments market will most likely exceed $1 trillion by 2032. The credit card acquiring trend won’t end anytime soon. Customers will continue using their cards to make different payments. But its functionality may be changed by new technologies.
Businesses must stay one step ahead of the latest trends to attract new and retain old customers. Leveraging new technologies can help merchants establish the strong safety policy required in a highly competitive market. The key trends include:
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine learning (ML) continue to progress, we can expect further innovations, contributing to both consumers and businesses through higher security, efficiency, and convenience. Get some insights on the innovations offered by AI and ML.
The impact of technology on card acquiring shouldn’t be underestimated. The tech developers aim to help e-commerce companies provide better accuracy, instant processing, cost efficiency, and improved customer support. AI and ML are probably the key innovations, although the range of opportunities is much more promising. Only those financial venues that implement these tech solutions can overcome bank card fraud and ensure customers’ safety.